

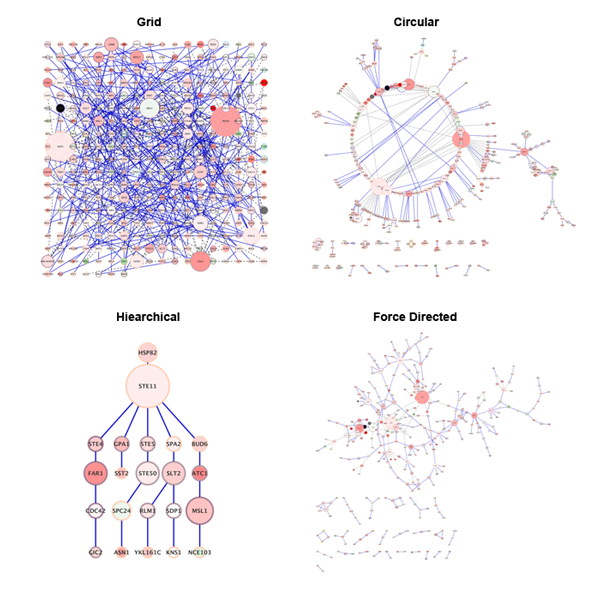
Layouts: Layouts provide a mechanism for automatically positioning nodes in a graph.
#DAGRE CYTOSCAPE FULL#
Cytoscape.js supports importing and exporting graphs via JSON, thereby allowing for full serialisation and deserialization of graph state. Import & export: The graph can be exported as an image (PNG or JPG), including at high resolution for publication. Compound nodes are useful for representing things like biological complexes and their subunits. ‘tap’ works both with computer mice and finger presses on touch devices.Īnimations: Animations can be used to increase the salience of particular elements in the graph and to provide visual continuity to the user when programmatic changes to the graph are made.Ĭompound nodes: As an addition to the traditional graph model, compound nodes are a way for the developer to embed nodes within another node. Several higher-level events are provided such that the type of user interaction is abstracted, e.g. for which elements and how many times the handler should be triggered) can be specified when binding. Bindings can be added and removed, and the multiplicity of elements-to-triggered-events (i.e. Delegation can be used such that newly added elements trigger bound events. The user can manipulate the viewport with gestures like pinch-to-zoom and drag-to-pan.Įvent binding: Events can be bound in several ways. Stylesheets can be replaced at runtime, changing the overall visual style of the graph.īuilt-in gesture support for mouse and touch based devices: The default Cytoscape.js renderer supports the touch and mouse gestures a user would expect out-of-the-box. node colour mapped from a numerical weight. et al., 2003), a functional mapper syntax is provided to map particular style properties based on element data-e.g. Similar to the Cytoscape desktop app ( Shannon P. Selectors and classes are supported in order to map element state to style.

Stylesheets: Stylesheets are used to specify the visual style of elements. Graph theory algorithms: Several well-known graph theory algorithms-such as connectivity search, shortest path, minimum spanning tree, minimum cut, ranking and centrality measures-are included. Graph traversal: Graph traversal functions are provided, which are useful for both user interface interactions and programmatic graph analysis. This enables apps to provide highly interactive graphs for the user. Mutable graphs: The graph can be manipulated by adding, removing, or modifying the state of graph elements. Graph types: Cytoscape.js supports several types of graphs, including traditional graphs, directed graphs, undirected graphs, multigraphs and hypergraphs (with compound nodes, but not yet with hyperedges). Some core functions take collections as input.Ĭytoscape.js features include, but are not limited to, the following: A collection has its own API that can be used to filter, traverse, perform operations on and get data about the elements in the collection. Each of these functions returns a collection, a set of graph elements. Core functions are available to access graph elements.
It represents the graph and is used to run layouts, alter the view, and perform other operations on the graph as a whole. The core is a developer’s main entry point into the library. The Cytoscape.js architecture is composed of the core and the collection. Similarly, graph elements are analogous to HTML DOM elements-they are styled by the stylesheets and programmatically accessible via the JS core API. Styling in Cytoscape.js is specified using CSS-like stylesheets, sharing as much syntax as possible with CSS. A GeneMANIA gene–gene interaction network automatically laid out and visualised with Cytoscape.js, showing interaction strength (edge thickness), interaction type (colour), multiple edges between nodes, protein score (node size) defined using a stylesheetįor increased ease of use, the library shares several concepts with the HTML + CSS + JS web model.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
